 Global| Oct 21 2003
Global| Oct 21 2003U.S. Budget Deficit a Record in FY 2003
by:Tom Moeller
|in:Economy in Brief
Summary
The U.S. Government budget deficit deepened to a record $374.2 billion in the fiscal year completed last month. That brought the deficit to 3.5% of GDP versus a peak deficit of 6.0% in FY '83 and surpluses from FY '98 through FY '01. [...]
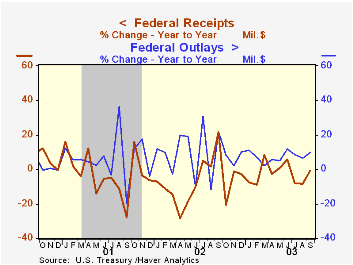
The U.S. Government budget deficit deepened to a record $374.2 billion in the fiscal year completed last month. That brought the deficit to 3.5% of GDP versus a peak deficit of 6.0% in FY '83 and surpluses from FY '98 through FY '01.
The Federal government's deficit fell short of recent projections for a $455B deficit in '03 due to sharp gains in individual and corporate tax receipts in September.
Net receipts for FY03 fell 3.8% versus last year. Individual tax payments fell 7.5% (roughly half the rate of decline in FY '02) and corporate income taxes fell 11.0%. Social insurance contributions rose 2.0% and excise taxes rose 0.8%.
Federal net expenditures rose 7.2% in FY '03. Defense spending surged 16.0% versus a 14.5% gain in '02. Growth in spending on health programs slipped to 11.6% from 14.3% in '02. Spending on education also slowed to a still-strong 16.4% from 24.1%. Growth in Medicare outlays picked up to 8.0% from 6.2% though growth in Social Security outlays slowed to 4.0% from 5.4%. Interest expense fell 10.6% versus a 17.0% decline in FY '02.
A report from the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco titled "The Fiscal Problem of the 21st Century is available here.
| US Government Finance | Sept | Aug | Sept '02 | FY2003 | FY2002 | FY2001 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Budget Balance | $26.4B | $-76.6B | $42.4B | $-374.2B | $-157.8B | $127.3B |
| Revenues | $191.6B | $114.3B | -0.5% | -3.8% | -6.9% | -1.7% |
| Outlays | $165.3B | $190.9B | 10.0% | 7.2% | 7.9% | 4.2% |
by Tom Moeller October 21, 2003
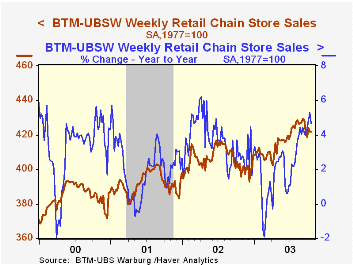
Chain store sales were about unchanged last week following the moderate dip during the week prior, according to the BTM-UBSW survey.
So far in October sales were down 0.4% from the September average which fell 0.8% versus August.
During the last five years there has been a 61% correlation between the year-to-year percent change in the BTM-UBSW measure of chain store sales and the change in non-auto retail sales less gasoline.
The BTM-UBSW retail chain-store sales index is constructed using the same-store sales reported by 78 stores of seven retailers: Dayton Hudson, Federated, Kmart, May, J.C. Penney, Sears and Wal-Mart.
| BTM-UBSW (SA, 1977=100) | 10/18/03 | 10/11/03 | Y/Y | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Weekly Retail Chain Store Sales | 422.0 | 421.9 | 4.6% | 3.6% | 2.1% | 3.4% |
Tom Moeller
AuthorMore in Author Profile »Prior to joining Haver Analytics in 2000, Mr. Moeller worked as the Economist at Chancellor Capital Management from 1985 to 1999. There, he developed comprehensive economic forecasts and interpreted economic data for equity and fixed income portfolio managers. Also at Chancellor, Mr. Moeller worked as an equity analyst and was responsible for researching and rating companies in the economically sensitive automobile and housing industries for investment in Chancellor’s equity portfolio. Prior to joining Chancellor, Mr. Moeller was an Economist at Citibank from 1979 to 1984. He also analyzed pricing behavior in the metals industry for the Council on Wage and Price Stability in Washington, D.C. In 1999, Mr. Moeller received the award for most accurate forecast from the Forecasters' Club of New York. From 1990 to 1992 he was President of the New York Association for Business Economists. Mr. Moeller earned an M.B.A. in Finance from Fordham University, where he graduated in 1987. He holds a Bachelor of Arts in Economics from George Washington University.






