German Inflation Sinks Lower

The inflation picture in Germany is improving rapidly. In November the HIPC measure fell by 0.1%; in October it fell by 0.2%; and in September it was flat. This is an impressive string of month-to-month weakness in prices. During the same period, the core HICP fell by 0.2% in November compared to October, it rose by 0.2% in October, while in September the core declined by 0.2%. Again, that's an impressive string of weakness in prices – this time in the less-volatile core prices.
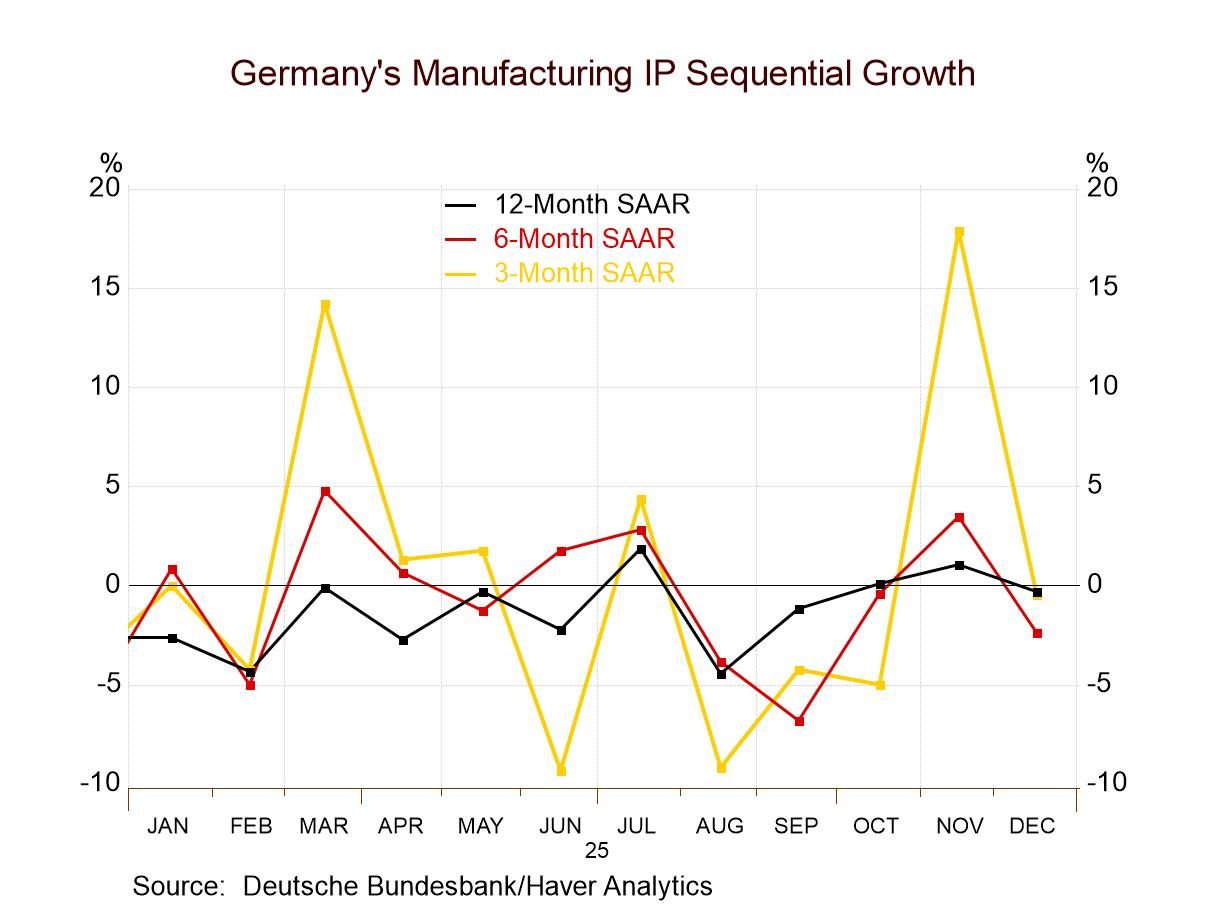
Sequential trends- Looking at sequential headline price trends from 12-months, to six-months, to three-months - at annual rates of change- inflation logged a 2.2% gain over 12 months, it edged up to a 2.7% pace over six months and then, over three months, prices fell at a 1.3% annual rate. Core inflation rose by 3.9% over 12 months, the six-month annual rate fell to 2.8%, and the core rate over three months annualizes to a minus 0.6% change. Inflation is controlled and largely falling. Will this trend remain in place?
A year-on-year focus- Central banks tend to emphasize the year-over-year rates of change in prices to be sure they are reacting to the trend and not to transient volatility. The year-on-year gain in the headline HICP for Germany is at 2.2%, the core is nearly double that at 3.9%. While there are no targets for country level inflation in the European Monetary Union, the German economy is a large economy and gets a very large weight in the statistics for the EMU. Germany's progression to lower rates of inflation is going to have an important and impressive impact on the EMU community.
The German domestic inflation gauge- The current domestic version of inflation has not been quite as favorable but the headline fell by 0.1% in November, was flat in October, and rose by 0.3% in September. The domestic German CPI excluding energy rose by 0.2% in November, rose by 0.1% in October, and rose by 0.2% in September. Its sequential annual rates for headline inflation, however, fall steadily from 3.2% over 12 months, to a 2.4% pace over six months, to a 0.7% pace over three months. That’s clearer deceleration than for the HICP headline measure. The German CPI excluding energy also shows a steady deceleration but logs inflation rates higher than those for the core HICP. The CPI excluding energy rises at a 4.1% annual rate over 12 months, at a 3% annual rate over six months and then decelerates to a 1.8% pace over three-months - still a nice progression of prices behaving- but not the same as the -0.6% three-month pace that the core HICP posts.
Diffusion signals are encouraging- Diffusion measures the breadth of the change in inflation across categories over the various periods. Over 12 months, the diffusion measure registers 45%, which tells us that inflation is accelerating in only 45% of the categories. Over six months, diffusion is 18%, which tells us that inflation accelerated over six months compared to 12 months in only 18% of the categories. Over three months, diffusion stood at 36%, telling us that inflation accelerated in only 36% of the categories over three months compared to six months.
Inflation signals showing progress reinforce one-another- Breadth statistics back up what's going on with headline and core inflation. Inflation is broadly falling and not accelerating; we see that both headline and core inflation rates are decelerating. These trends echo trends that we see in the United Kingdom and in the United States. Inflation progress is being aided by weakness in global oil prices. OPEC as well as OPEC-plus have not been able to cut back output fast enough to stabilize oil prices. Measured in euros, the Brent oil price is down by 15% over 12 months; it rises at an 18.3% annual rate over six months, but then it’s falling at a 9.4% annual rate over three months. Brent prices expressed in euros fell by 9.2% month-to-month in November after falling 2.9% month-to-month in October; those progressions followed a 10.7% increase in September. Oil’s contribution is erratic.

Global forces are in play- Weakening global growth appears to be having an impact on global commodity prices and oil prices as well as the general effect on national price levels. However, the measure for inflation that central banks emphasize is the 12-month inflation rate. The progression for inflation over shorter periods is showing a clear -and in some cases - dramatic decline in the rate of inflation. Central banks have been slow to embrace the recent inflation decline having made one inflation mistake in this cycle already; some of them don't think they can afford to make a second inflation mistake, so they're waiting to make sure that this short-term price weakness reduces the pace of inflation on a year-over-year basis to their target or at least much closer to their target before they reverse policies and take their foot off the brake.
The Road Ahead- Still, we have to consider central bank policies in the U.S., in the EMU, and in the United Kingdom as being difficult to characterize since central banks contributed so much to the inflation. They were so slow to raise rates and did not raise them as much as they did in the past when inflation emerged. Now that inflation is falling, they hardly have any choice but to make sure that inflation is going to be under control before they start cutting interest rates. Central bank credibility has taken a huge hit in this cycle as banks joined too vigorously to buffer the economies from the effects of Covid. As a result, the combination of fiscal and monetary stimulus, in addition to the unexpected impact of war, created a huge inflation rate that central banks have had a hard time getting in front of. They may now be in front of it. But they seem to be playing a much more careful game when it comes to their own perception of how much in control they really are.
Robert Brusca
AuthorMore in Author Profile »Robert A. Brusca is Chief Economist of Fact and Opinion Economics, a consulting firm he founded in Manhattan. He has been an economist on Wall Street for over 25 years. He has visited central banking and large institutional clients in over 30 countries in his career as an economist. Mr. Brusca was a Divisional Research Chief at the Federal Reserve Bank of NY (Chief of the International Financial markets Division), a Fed Watcher at Irving Trust and Chief Economist at Nikko Securities International. He is widely quoted and appears in various media. Mr. Brusca holds an MA and Ph.D. in economics from Michigan State University and a BA in Economics from the University of Michigan. His research pursues his strong interests in non aligned policy economics as well as international economics. FAO Economics’ research targets investors to assist them in making better investment decisions in stocks, bonds and in a variety of international assets. The company does not manage money and has no conflicts in giving economic advice.
More Economy in Brief
 Global| Feb 05 2026
Global| Feb 05 2026Charts of the Week: Balanced Policy, Resilient Data and AI Narratives
by:Andrew Cates