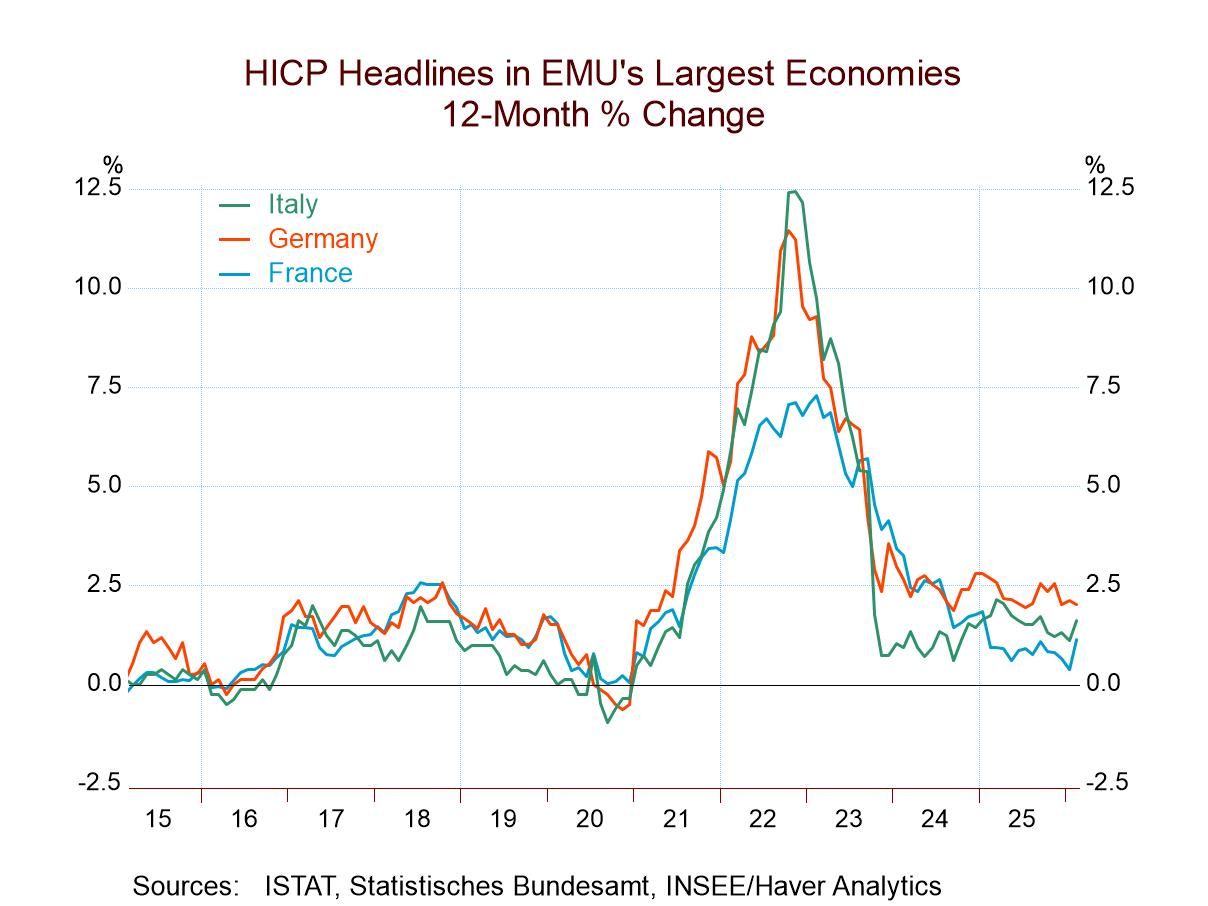
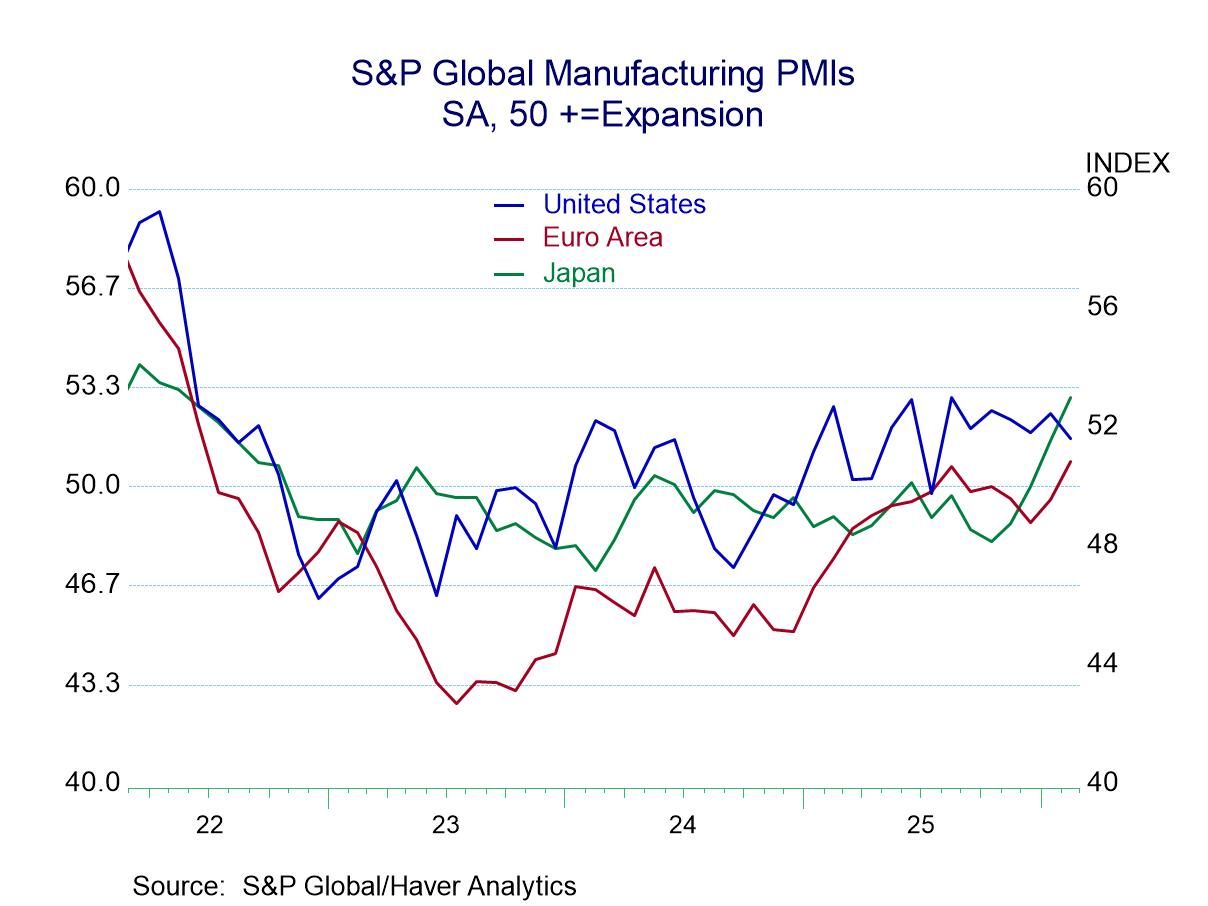
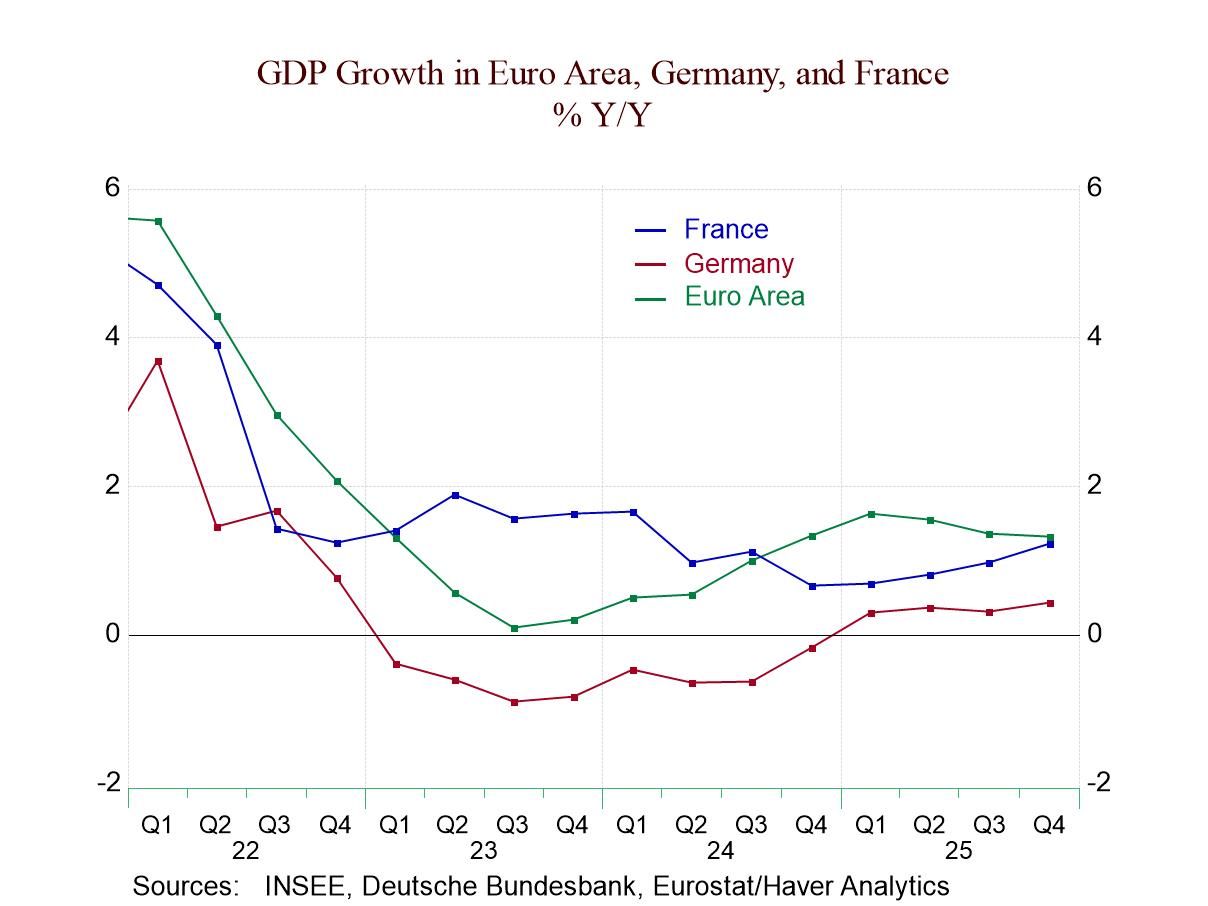
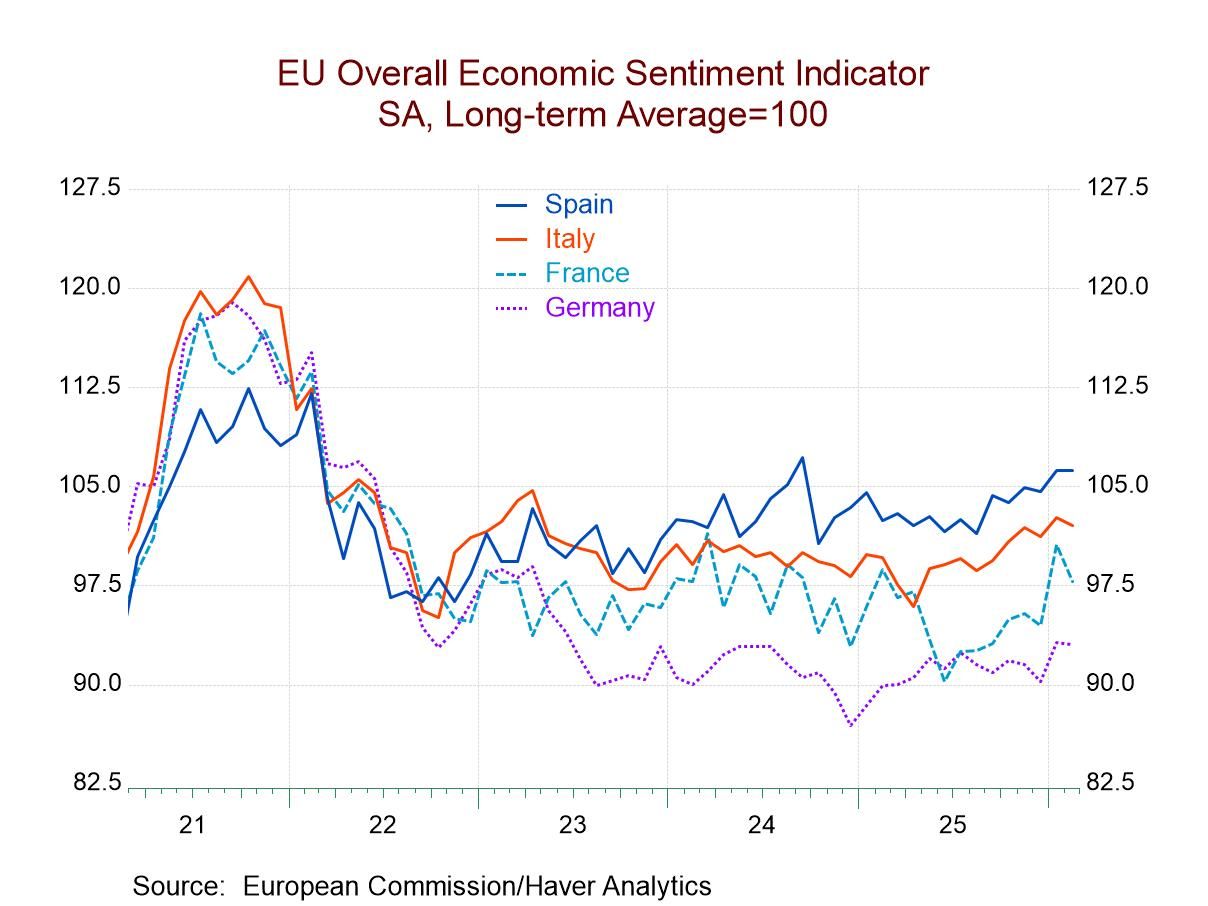
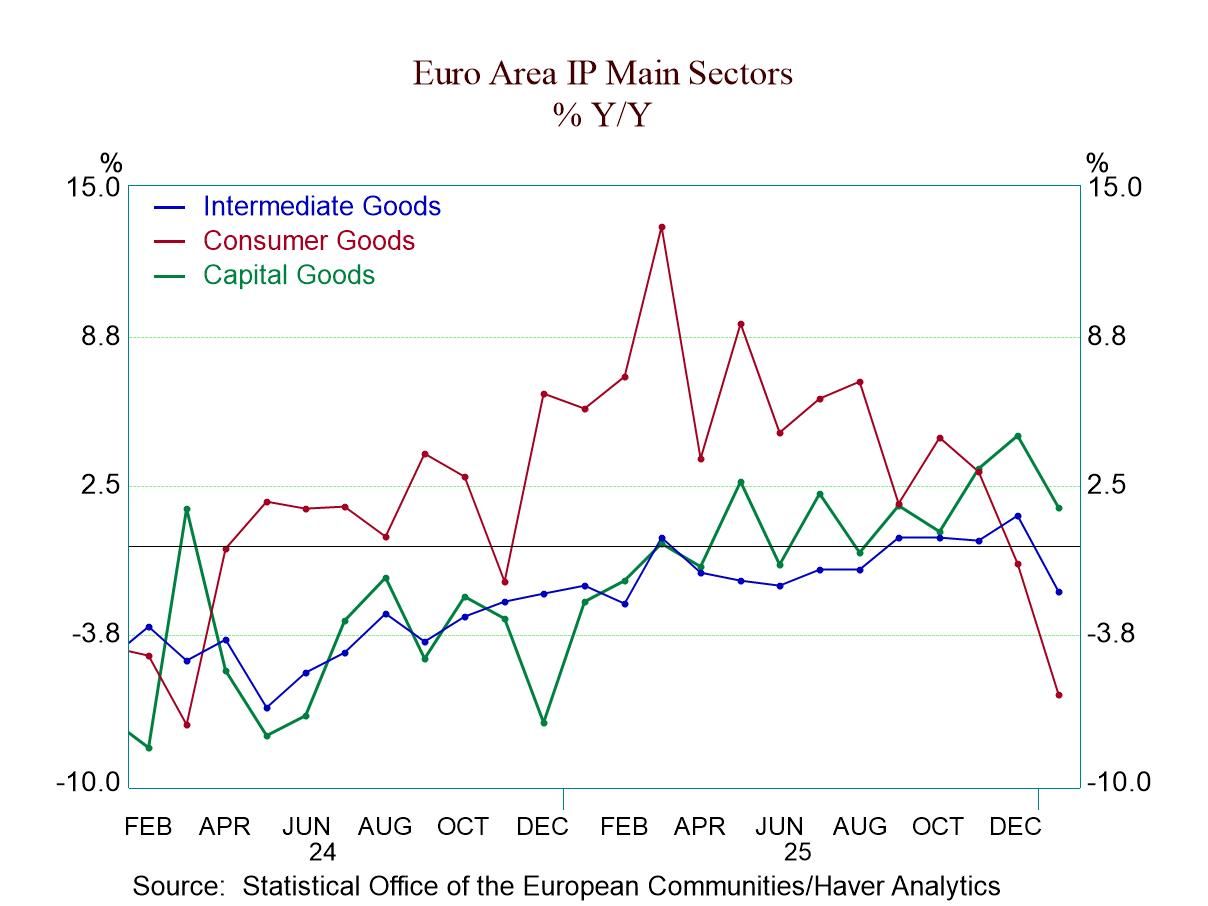
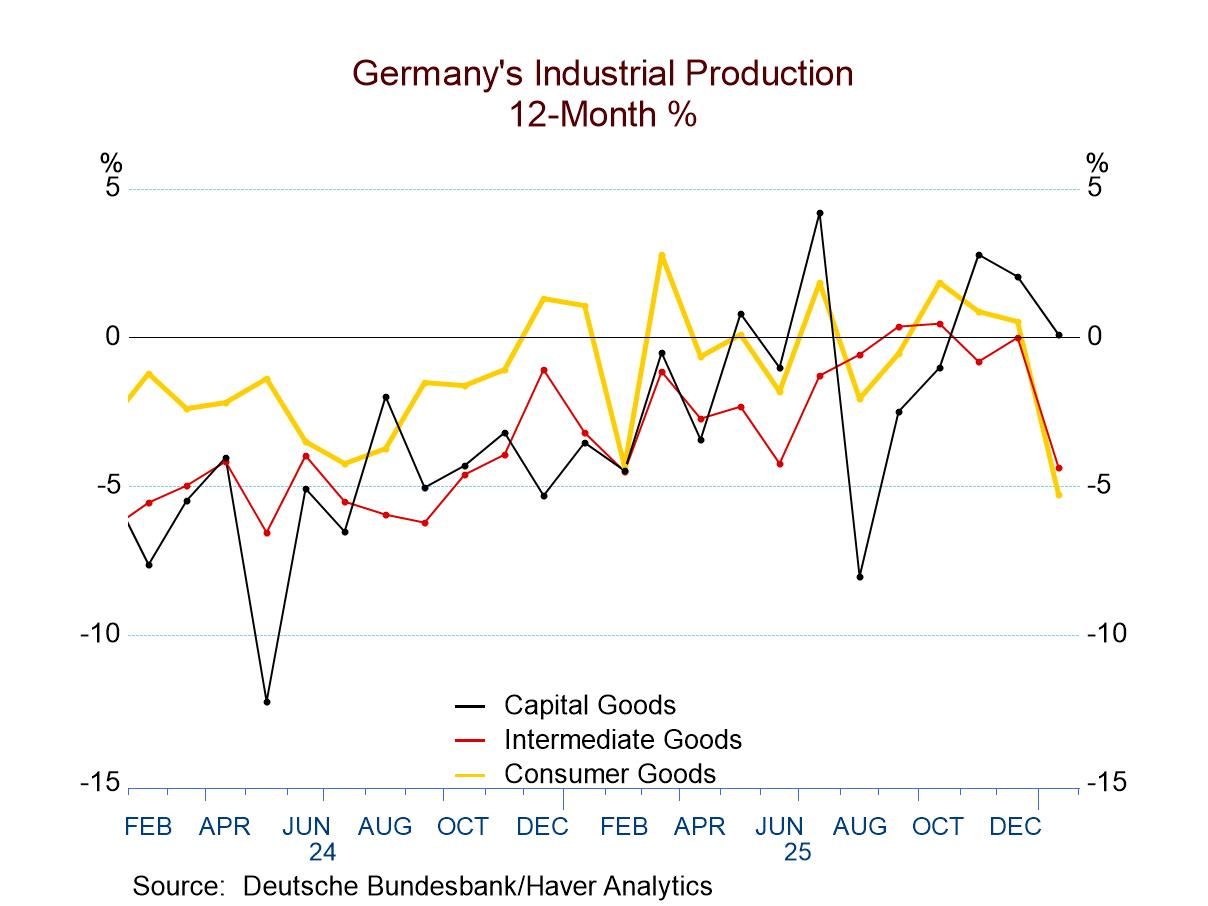
Broad and severe weakness in European production: industrial production data for the monetary union turned decidedly sour in January. All major production categories showed declines in January, including the headline series for production excluding construction and manufacturing output. There were also drops across the major manufacturing sectors—consumer goods, intermediate goods, and capital goods—as well as in both of the consumer sub categories of durable goods and nondurable goods. January was a really tough month for the industrial sector and the European monetary union.
Sequential output weakness as well: Output is not only falling in every category in January—and for two months in a row—but the sequential growth rates over 12 months, six months, and three months also show decelerations present for all of these categories of output except capital goods. That means the six-month growth rate is weaker than the 12-month growth rate, and the three-month growth rate is weaker than the six-month growth rate for six of seven of these categories—the exception is capital goods. And capital goods are a minor exception with the growth over three months only slightly stronger than over six months, and at that it's still a negative growth rate. It shows a decline in output, just a slower decline. There is no silver lining here, just clouds and rain.
Quarter to date and more: As if that's not enough, these are output data for January so we can calculate quarter-to-date growth rates in the first quarter. On that basis, all seven of these categories show output declining, and output is declining in all seven of these categories at a double-digit pace! In addition, when we step back to compare growth rates over the last year with previous 12-month growth rates back to April 2006, a 20-year horizon, we find that all the growth rates in the table lie below their median rates of growth for this previous twenty-year span. Capital goods fare the best, with a percentile standing of its growth rate at its nearly 48th percentile, just slightly below its median, which lies at a ranking of 50%. The growth rates for consumer nondurables, for example, have had output growth weaker during this period, only 1.7% of the time. Consumer goods output has been weaker, only 3.8% of the time. Manufacturing output is in the bottom quartile among historically ranked growth rates. These are extremely bad and consistently poor rankings for industrial growth.
The table also offers up country-by-county data for January. Looking just at monetary union members, seven of twelve show output declines in January, but that compares to December, which was a strong month with only three of those members showing output declines. However, a month earlier, in November, eight monetary union members had shown output declines. There are sequential output declines reported by Germany, Spain, and Ireland over the last twelve-to-six-to-three months. Only Malta and Greece show output trends that are accelerating, and of course, these are two of the smaller monetary union countries. Seven monetary union countries show quarter-to-date output is declining early in this first quarter. Among the five countries showing output increasing, two of them showed double-digit growth rates in the new quarter and those two again are Malta and Greece. For the countries overall, only five of twelve have queue percentile standings of their earlier growth rates that are above their historic medians for the last 20 years. That list of five includes France, Malta, Greece, Portugal, and Austria.
The industrial data for Europe in January are decidedly downbeat and concerning. These numbers are being reported before hostilities in the Middle East began to ramp up and clearly before oil prices spurted higher. The European manufacturing sector is not digging itself out of the hole it fell into after COVID and the invasion of Ukraine. And after showing a hint of recovery, it now appears to be deep in the morass of economic weakness.



 Global
Global