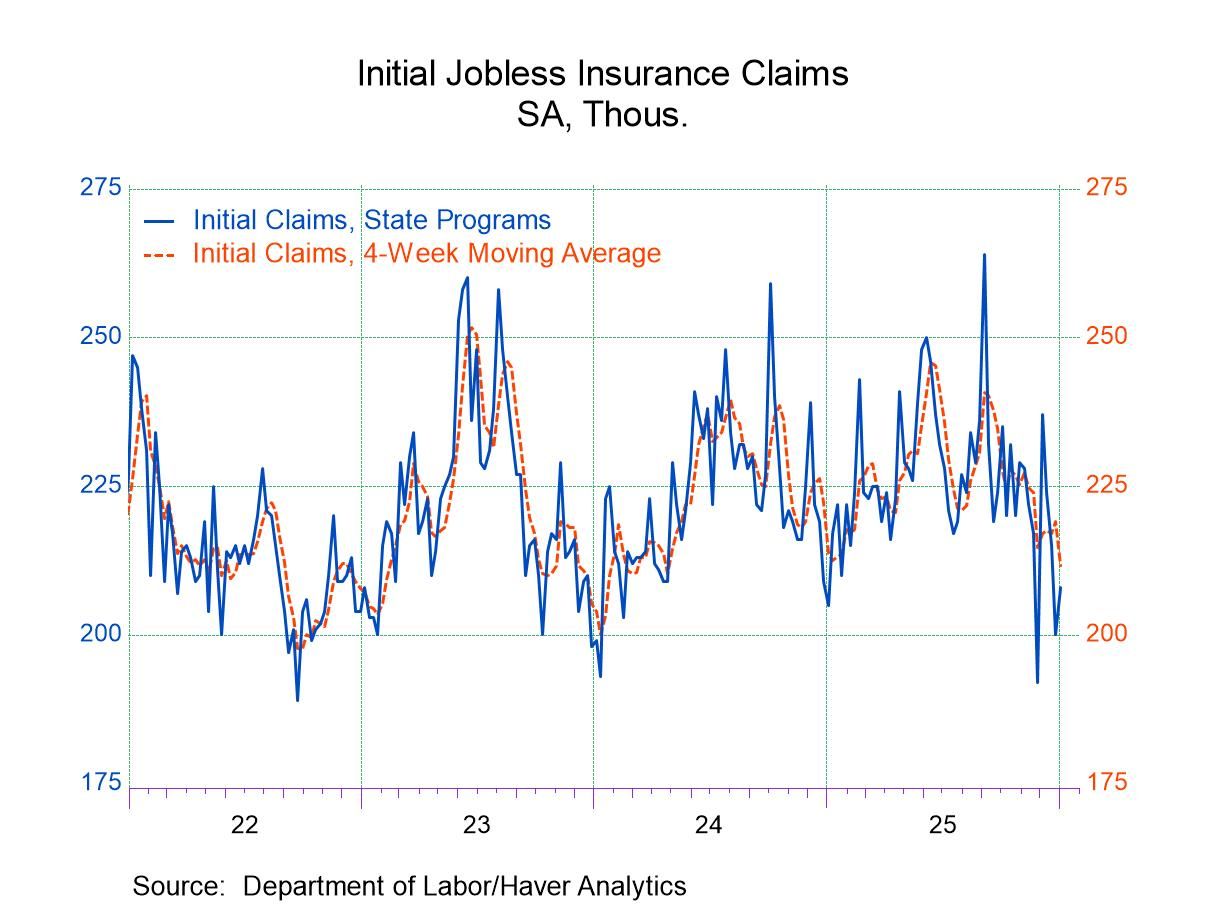
- Initial claims rose moderately from the prior week.
- Continuing claims increased from the prior week.
- The insured unemployment rate was unchanged.
- Europe| Jan 08 2026
EU Indexes for EMU Weaken at Year-End
The EU indexes for December 2025 showed slight slippage as the overall index fell to 96.7 from 97.1 in November for the whole of the European Monetary Union. Sectors showed slippage in consumer confidence and retailing; confidence slipped to -13.1 in December from -12.8 in November as the retail rating slipped to -7 in December from -6 in November. The services sector and the industrial sector were each unchanged on the month, with the industrial reading at a net standing of -9 and the services reading at +6. Improving month-to-month was construction where the index rose to a -1 in December from -2 in November.
Queue standings of sectors The queue (or rank) standings for the overall reading as well as the sector readings largely cluster around the lower one-third of the range of values on data back to 1985, where applicable. Retailing and construction are exceptions, with retailing at an above-median standing at a 51.3 percentile and construction at a solid and strong 81.6 percentile standing in December. The weakest reading is for consumer confidence at the 23.1 percentile standing followed by the industrial sector at a 30.5 percentile standing; services check in at a 37.9 percentile standing. The rank standing for the overall monetary union is at 34.4%, just slightly above the bottom one-third mark for all ranked observations over the period.
Country results 18 countries report detail in this survey. Seven of the 18 showed declines in December; this is up substantially from November when five showed declines and compares to October when eight countries showed declines. An unfortunate feature of December is that the headline reading for the monetary union weakens as well as readings for each of the four largest monetary union economies Germany, France, Italy, and Spain.
The two largest monetary union economies, Germany and France, have the weakest rank standings among the BIG4 with Germany at a 15.7 percentile standing and France at a 29.5 percentile standing. Italy and Spain each have standings above the 50% mark placing them above their medians for Italy with a reading of 54.2 percentile, while for Spain it's a 61.2 percentile standing.
Standings across smaller economics Across the remaining monetary union countries, six of the 14 readings are above their 50th percentile, while eight of the 14 are below their 50th percentile. Well, the large countries are experiencing a significant split; the rest of the monetary union appears to be in much the same condition, with approximately half of them performing at above-median conditions and half performing at below-median conditions.
Country stories The chart of the monetary union indexes by sector shows us that there has been little change and little trend in these observations. Across countries Germany has definitely been the weakest country among the BIG4, while Italy has been the strongest. Inflation data have showed inflation beginning to heat up in Spain, and Spain does have the strongest queue standing among the four largest monetary union economies - so that might be something to keep an eye on going forward. Conditions in Germany and France are still quite weak and seem unlikely to force an increase in inflation.
Smaller economies- some specifics And so, the rest of the monetary union economies show tiny Malta, which is hardly a price-maker, has a strong 99.6 percentile standing, followed by 70th percentile standings in Greece and then Lithuania. Portugal and Cyprus have readings in their 60th percentiles. For the most part, these are modest readings but above their medians, of course. Among the weak economies in the rest of the union, the weakest is Belgium with a 16.9 percentile standing, followed by Estonia at a 28.4 percentile standing, Luxembourg at a 32.8 percentile standing, and Austria at a 33-percentile standing. After that, Finland’s standing goes to 37.7 percentile with the Netherlands, Slovakia, and Latvia all with readings in their 40th percentiles indicating moderate undershooting relative to their respective medians.
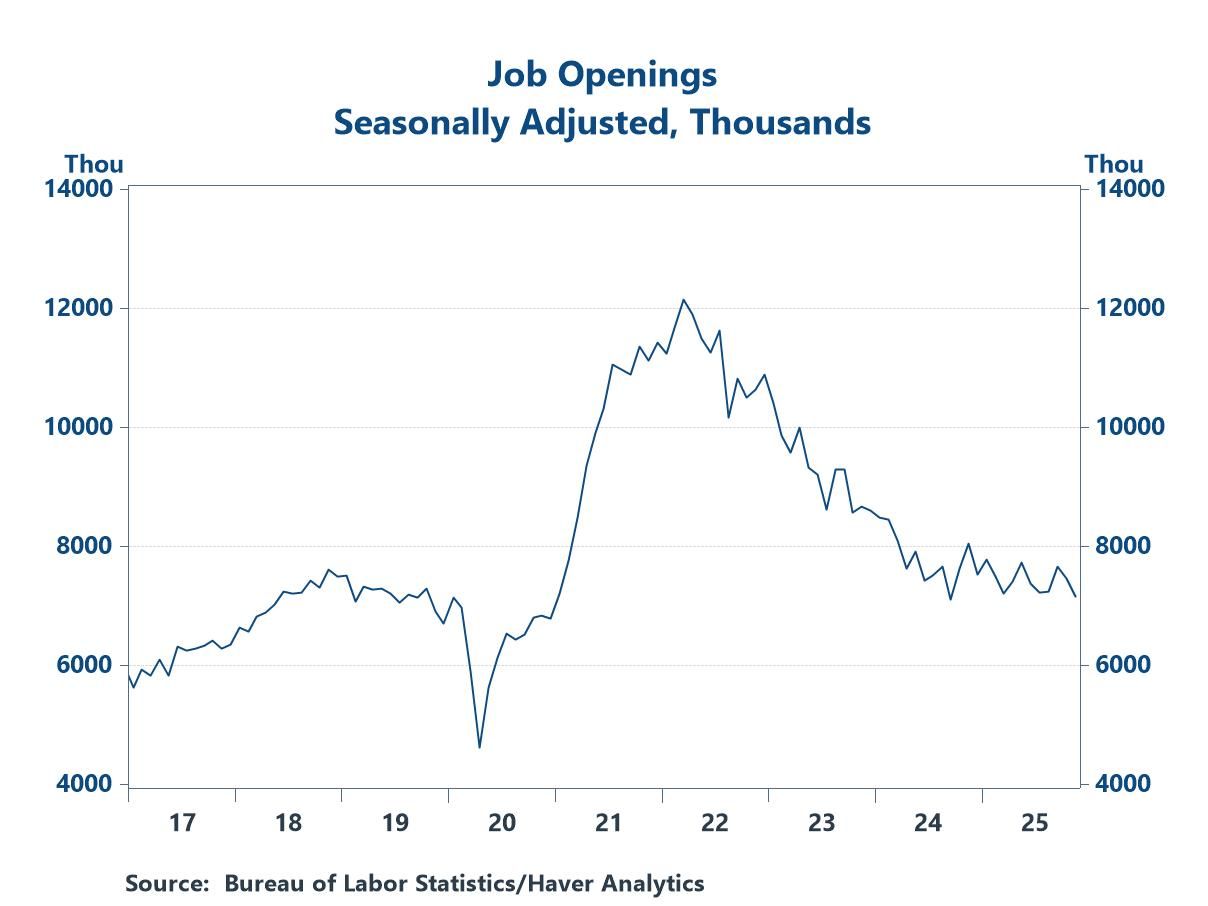
- Job openings have eased considerably from the elevated levels seen during the post-pandemic recovery, but they are in line with pre-pandemic norms.
- Businesses are not rushing to fill posted positions.
- USA| Jan 07 2026
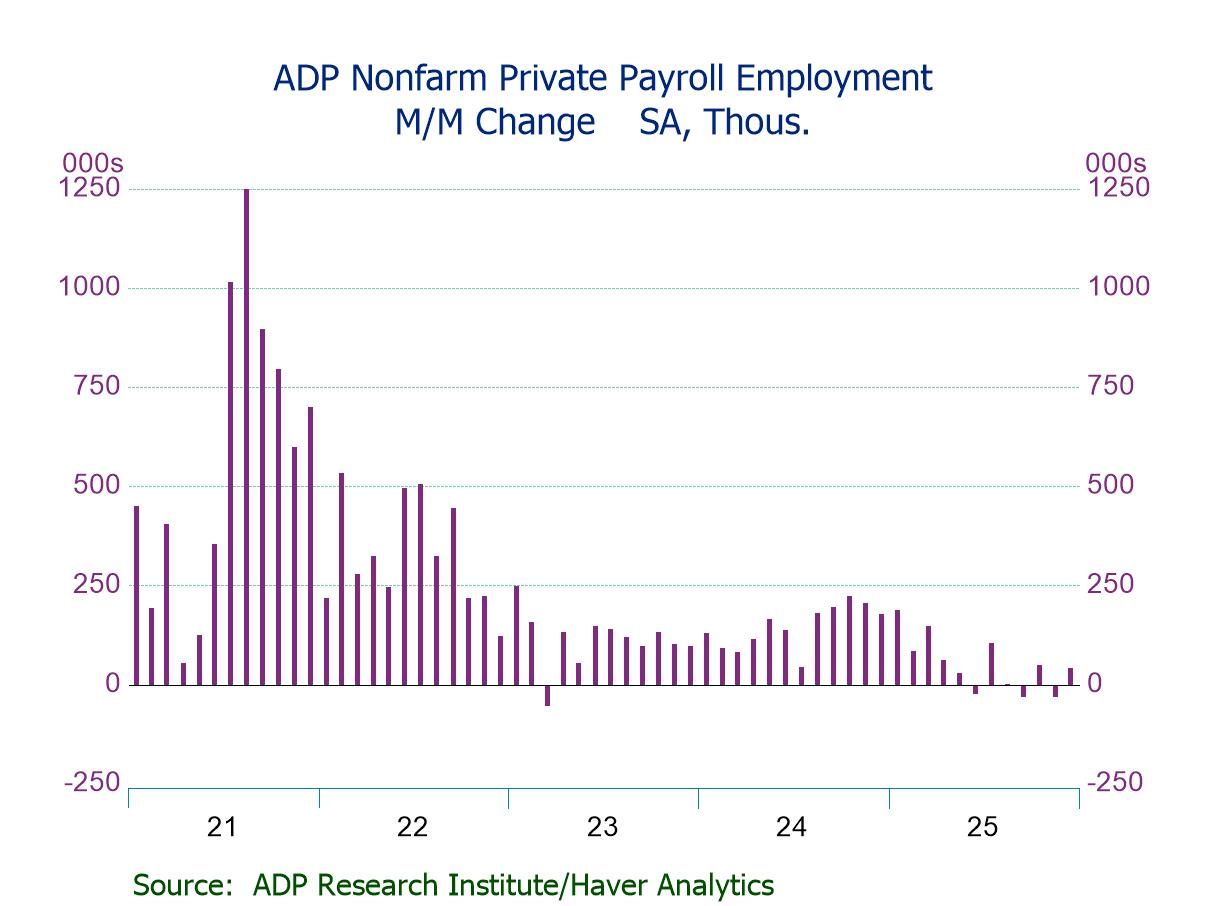
U.S. ADP Private Employment Rebounds in December
- Private payrolls +41K; second m/m increase in three months.
- Hiring increase is driven by medium-sized businesses (+34K).
- Service-sector jobs up (+44K), led by education & health svs. (+39K) and leisure & hosp. (+24K); goods-producing jobs dip (-3K).
- Wage growth accelerates y/y for job changers (6.6%) but steady for job stayers (4.4%).
- USA| Jan 07 2026
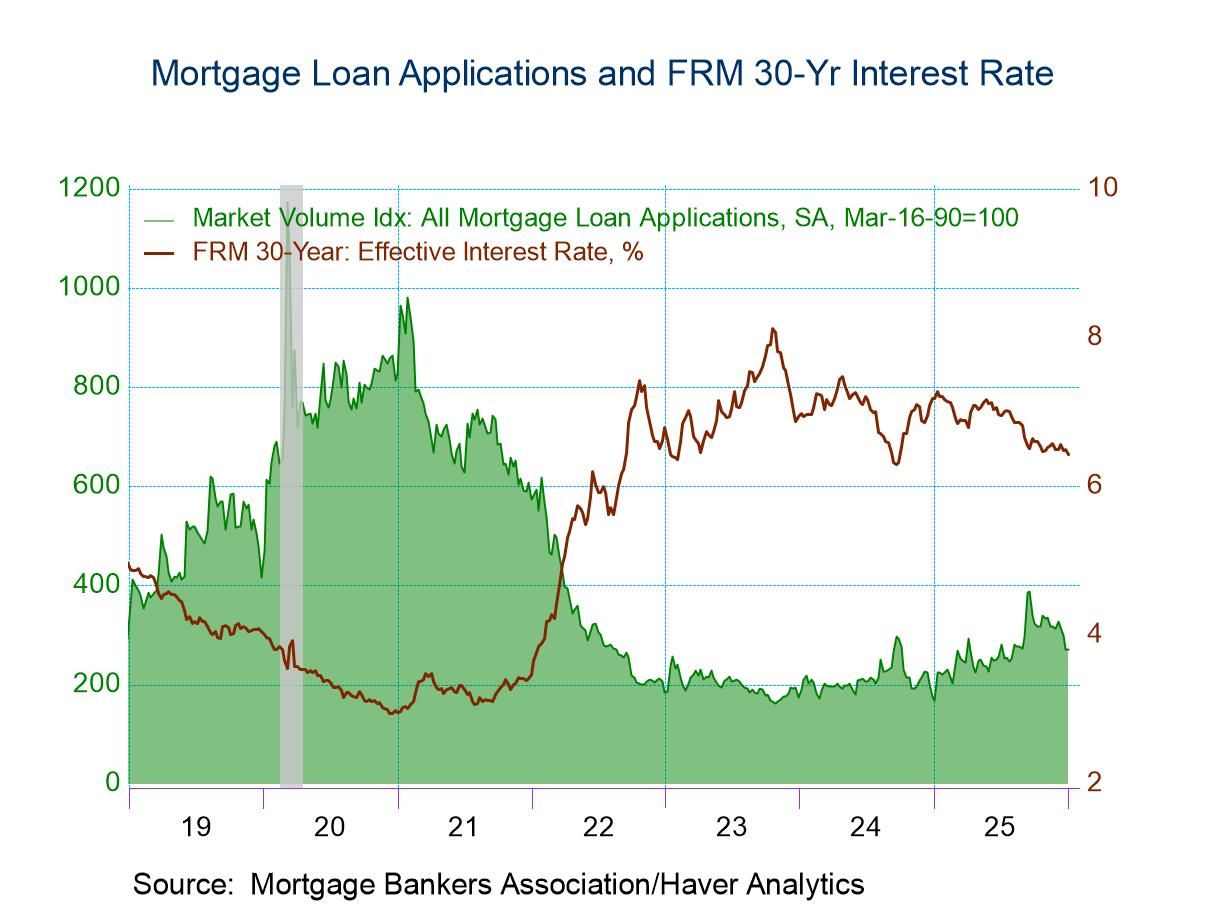
U.S. Mortgage Applications Edged Up in the Week of January 2
- Purchase applications dropped while refinancing loan applications rose in the latest week.
- Effective interest rate on 30-year fixed loans fell to 6.42%.
- Average loan size declined.
 Global| Jan 07 2026
Global| Jan 07 2026Inflation in the Euro Area Is Warm but Well-Behaved at Year-End
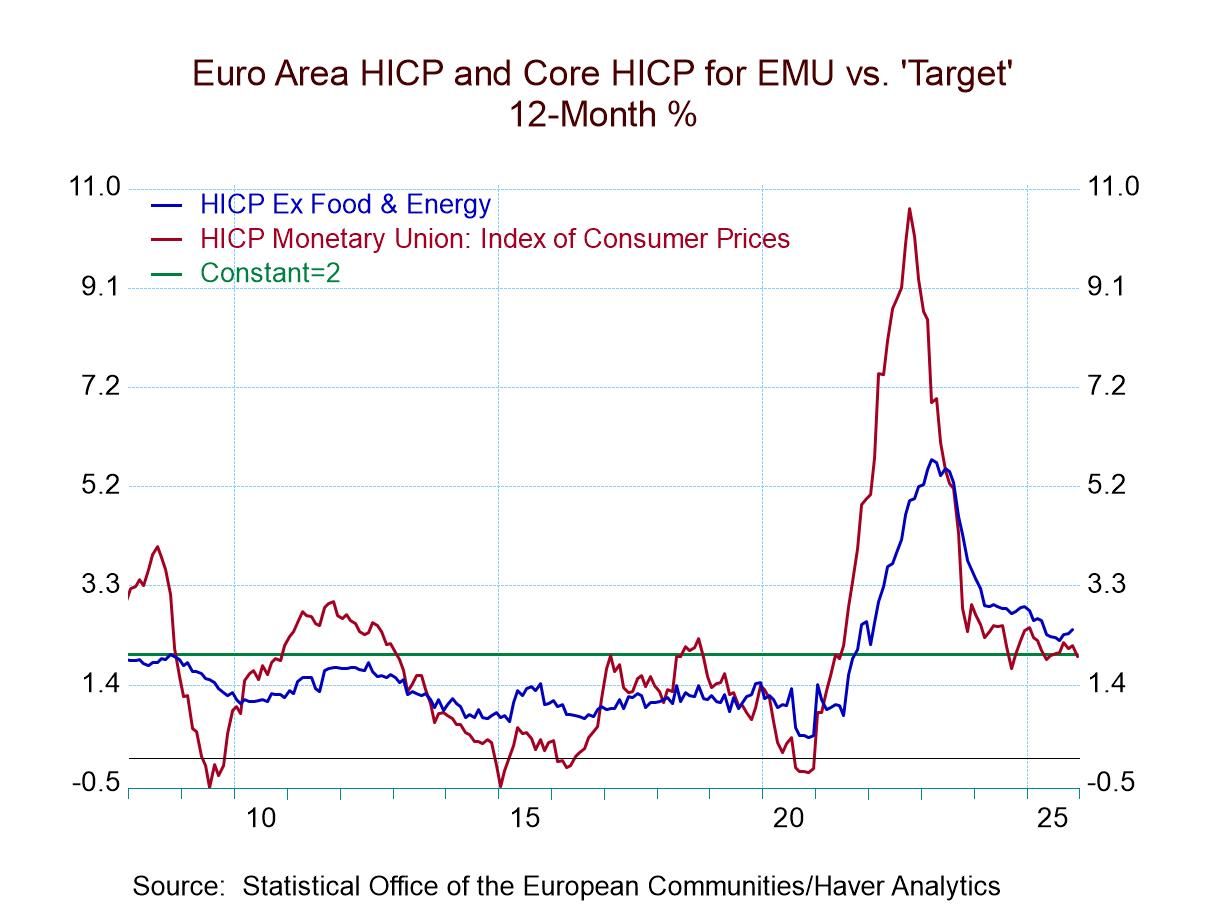
Inflation in the euro area as 2025 draws to a close has pretty much behaved. The HICP gauge for the European Monetary Union, that's targeted at a pace of 2% is closing the year with a 12-month pace of 2% which is exactly what the ECB is looking for. Success is at hand! Congrats to the ECB!
It’s like the super bowl playoffs: a victory, but more games lie ahead However…oh yes there is almost over an ‘however’ or ‘none-the-less’ or some other insidious phrase inevitably is inserted to introduce a caveat… and that is this: over six months the headline pace is at 2.4% at an annual rate, and over three months the pace is at 2.2% at an annual rate. Still, the year-over-year inflation rate is how central banks normally are judged and it has come in right on target, and the ECB can claim a large measure of victory for that even as it faces the challenge for 2026.
Visiting 2% or setting down roots? At the same time, inflation is only closing in on the 2% target over other horizons. It has not generally proven itself to be stable at 2%, having spent most of its time at a pace above 2% for the past year as the chart shows.
So far so good... The monthly numbers have been encouraging with the December gain in the HICP at 0.2%. Germany logged a gain of 0.1%, month-to-month, France and Italy had gains of 0.2%, while Spain is at 0.4%. Spain, where inflation had been pretty-well contained, has now moved over to the rogue side of the ledger. Spain posted inflation at 3% year-over-year, at a 4.5% annual rate over six months, and at a 5.7% annual rate over three months. Other monetary union countries showed more disciplined patterns. For example, France has a 0.7% gain year-over-year with a 1.2% annual rate gain over six months, and a 1.1% annual rate gain over three months. All of them, of course, are gains well within the ECB's desired result for the union as a whole. Italy shows a tendency toward deflation at a 1.3% HICP gain over 12 months that shifts to a decline of 0.3% at an annual rate over six months, and to a decline of 1.9% at an annual rate over three months. The other troublesome country among the Big-Four economies in EMU is Germany where the 2% headline achievement over 12 months is right on top of the target the ECB seeks; however, it gets there with a 3.1% annual rate increase over six months and a 4% annual rate of increase over three months. Both of those gains, of course, are over the line and indicate accelerating inflation even as German inflation ends the year at 2% and is ‘seemingly’ compliant.
Core inflation is a slightly different animal Germany gives us an early look at inflation excluding energy. Italy and Spain give us core measures to look at early in the year. The December results show ex-energy inflation in Germany at 0.1% month-to-month, Italian core inflation at 0.3%, and Spanish core inflation at 0.2%. This followed a batch of similarly well-behaved numbers in November for these three countries (see Table). The core sequential inflation rates are generally better behaved for these three countries than for their headline rates. Germany's metric excluding energy comes in at 2.2% for the year but it accelerates at a 2.7% pace over six months and then it's back down to 2% over three months. Italy shows a compliant 2% pace over 12 months, then it slides to a 1.5% annualized over six months and slips further to a 0.7% pace over three months, echoing the deflation trend that we see in Italy's headline pace. For Spain, the core also exhibits accelerating inflation trends to join what it reports for the headline as the year-over-year core pace is at 2.6%, the six-month rate steps up to 3.1% annualized, and stays in that neighborhood at a 2.9% annualized rate over three months.
 Global| Jan 06 2026
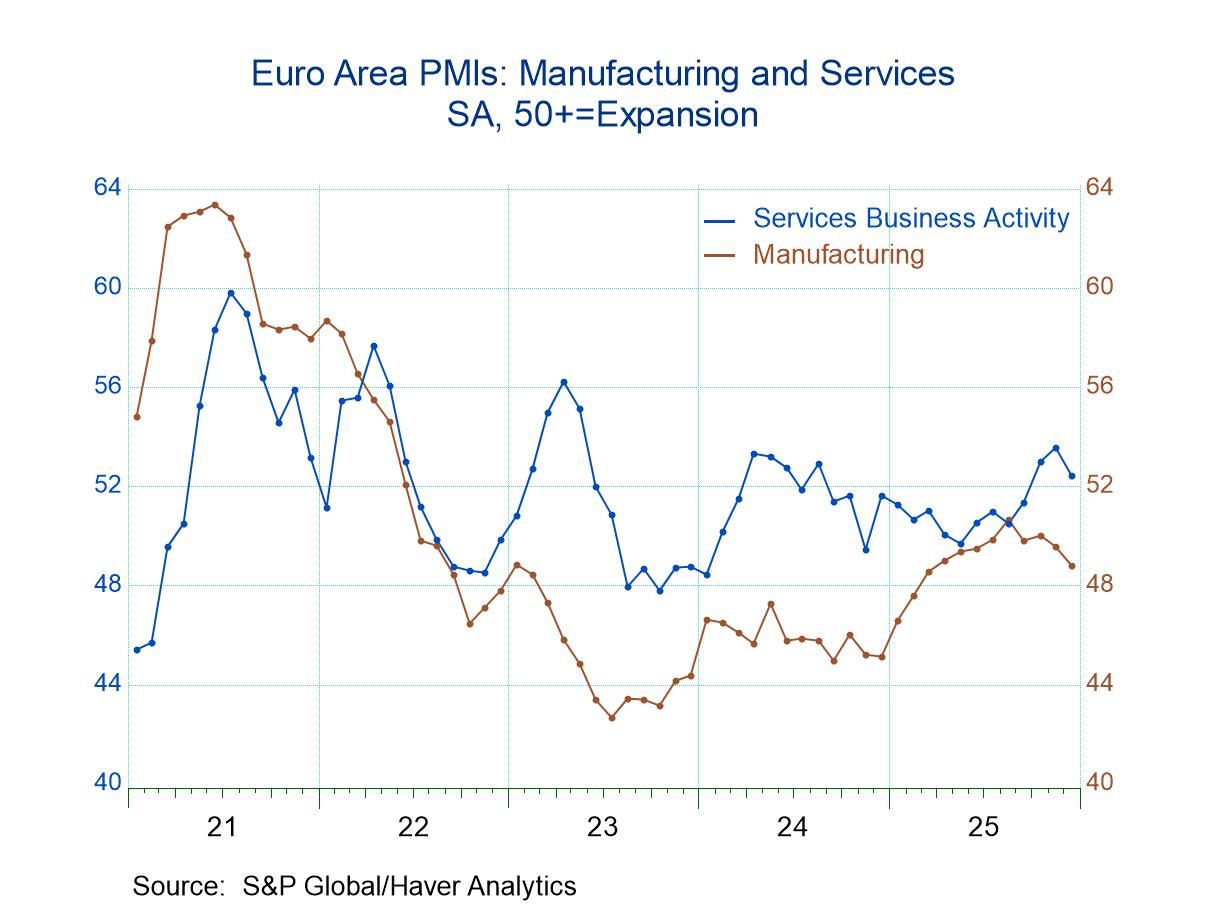
Global| Jan 06 2026S&P Total PMIs A Mixed Bag As 2025 Ends
The S&P total or composite PMIs demonstrated a tendency to weakness in December as 64% of the 25 reporting countries reported weaker readings in December than in November. However, even with that bit of bad news on the table, the number of jurisdictions that reported PMI readings below 50 indicating economic contraction had gone to zero, indicating that there were no contracting jurisdictions in December. That's an improvement from two contracting in November and three in October. In those previous months, for example, in October, only 36% of the reporting entities were weaker month-to-month; in November, only 40% were weaker month-to-month so the step up to 64% weaker month-to-month in December was a big step-up in weakness; however, it comes after a period when conditions had generally been improving and now that has stopped.
Sequential trends: 12-months to 6-months to 3-months Sequential data that look at performance over three months, six months and 12 months compared to earlier periods show that, over three months only 34.8% of the jurisdictions were weaker compared to six-months. Over six months only 26.1% were weaker compared to 12-months. However, 12-months was a period of treading water because over 12 months compared to 12-months ago, about 48% of the reporters were weaker indicating that conditions over the past year had been largely unchanged. But over shorter periods of time conditions had been improving.
Contraction is less common At the same time, sequential data showed that there has been an improvement in terms of the number of jurisdictions that are showing contraction because there were five of them over 12 months, four of them over six months and only two of them over here months.
Standings/rankings The queue percentile standings show eight jurisdictions below 50% which means that on data from January 2021, only eight of the twenty five reporters are below their median result for that period. Egypt, Kenya, Sweden, and the United States have percentile standings in their 90th percentile marking them as very strong composite standings compared to where they have been over the last five years. There were also strong rankings in a relative sense in Western Europe with the European Monetary Union in its 81st percentile, Germany in its 81st percentile, France in its 81st percentile, and Hong Kong in its 83rd percentile, indicating strength spread across various areas but concentrated in Europe. On the weak side, there are extremely weak readings that are offered by Qatar that has an 11.9 percentile standing, in India that has a 19-percentile standing, the UAE with a 31-percentile standing, and China with the 38th percentile standing. These are relative standings that is they are not a ranking of the PMI values compared to other countries, but rather comparing to each individual country over the whole time series of values since January 2021 with its own performance. China, for example, has a 51.3 composite reading for December 2025, and while that's roughly a lower 1/3 reading compared to where it's been historically, it isn't a particularly weak reading compared to what other countries are reporting in December 2025. China, for example, ranks 17th out of 25 countries (approx. bottom one-third position) reporting data in December 2025. In the case of China, its timeseries and cross-section standing are very similar in ranking terms.
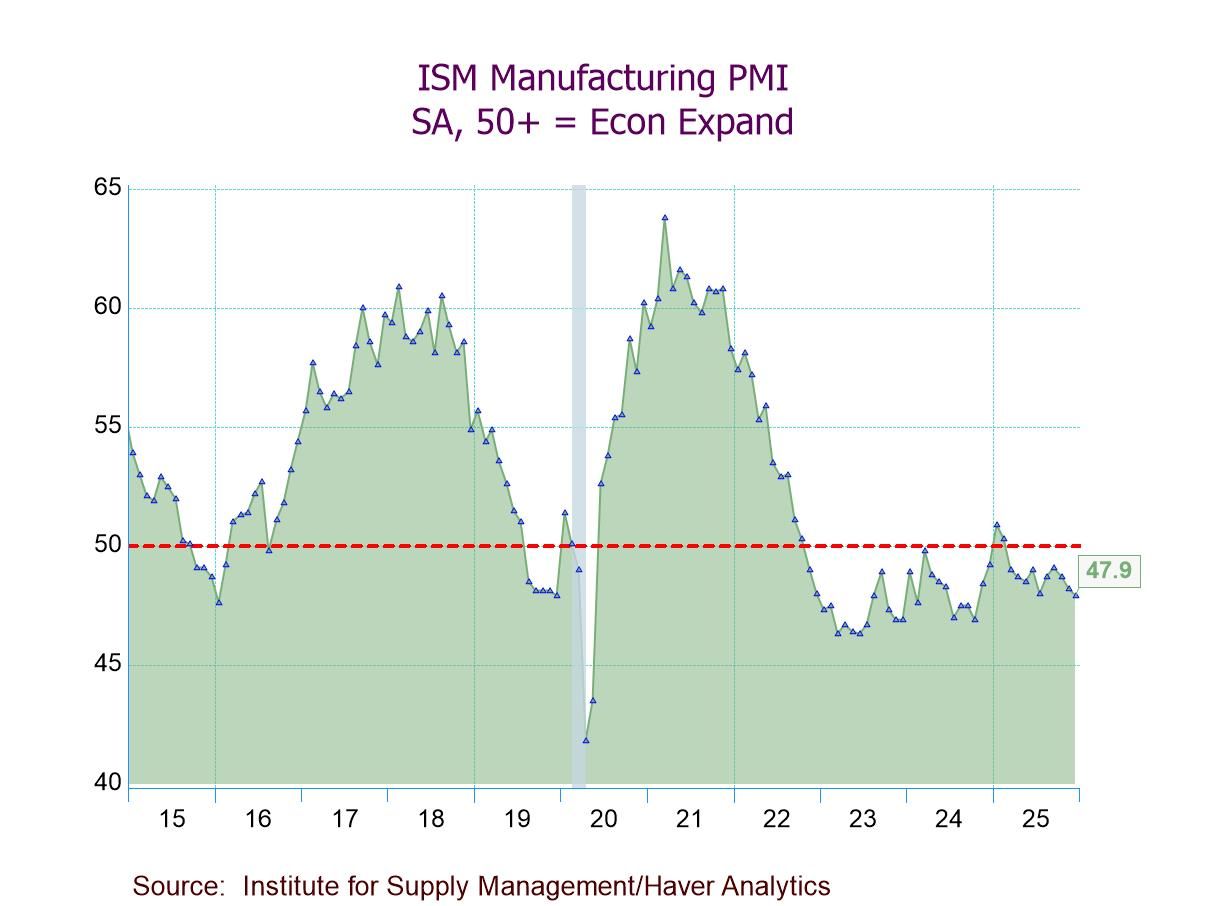
- ISM Mfg. PMI down to 47.9 in Dec., below forecasts; 10th straight month of contraction.
- Production (51.0) expands for the third time in four months.
- New orders (47.7) contract for the fourth successive month.
- Employment (44.9) contracts for the 11th consecutive month.
- Prices Index (unchanged at 58.5) indicates prices rise for the 15th straight month; exports & imports continue to contract.
- of2693Go to 8 page