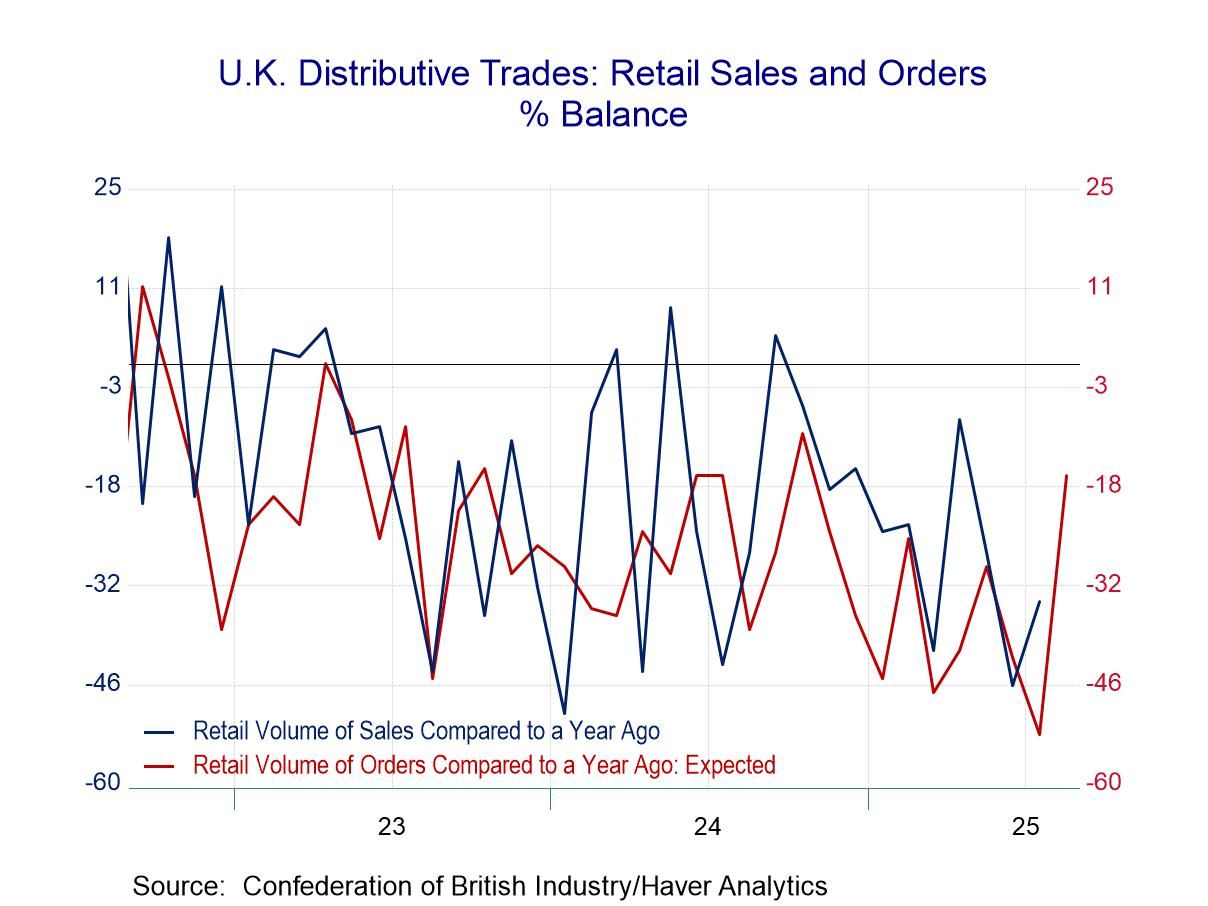
The severe lethargy in U.K. retail and wholesale sales continues into July with the outlook portion of the survey for August still exceptionally weak.
Distributive sales retail volumes Sales in July: In July, the distributive trades volume survey finds sales for a year ago with 34% of the respondents indicating weaker sales compared to those indicating stronger sales. This net reading of -34 is a slight improvement from June’s -46 and signals deterioration compared to May (-27) as well. However, beyond the monthly bumping up and down, the ranking of this net reading is in the lower 8.5 percentile marking it as truly an exceptionally weak reading. The reading for orders compared to a year ago shows better comparisons but still a great deal of weakness and a net reading of -21, compared to -51 in June and -41 in May. It marks a 20th percentile standing, which is better than for sales compared to a year ago but still exceptionally weak. The next reading that, essentially is seasonally adjusted, comparing sales for the same time of year, shows a -10 reading which is better than -37 in June and better than May’s reading of -19 and steps up to a percentile standing at its 42nd percentile. It is still short of its median (which occurs at a ranking of 50%) but is a reading that looks a little closer to the land of the living than the land of the dead.
Expected sales in August: The distributive volumes statistics for sales expected for August, looking a month ahead, shows negative readings across the board for these same 3 metrics with all three of them improving in August from their July expectations; however, sales compared to a year ago have a 7-percentile standing, even weaker than their current July reading, orders have a 23.5 percentile standing, and sales for the time of year fare much worse with a 6.7 percentile reading - much worse than the current performance ranked for July. In short, there's very little in this survey that is encouraging or reassuring. Conditions are weak and even where there is improvement the new reading is still very weak and the expectations readings, while somewhat improved, are still extremely weak.
Distributive sales wholesale volumes Sales in July: The distributive trades survey for wholesaling produces another set of weak readings that are, for the most part, weaker in July than they were in June and, while different, not much better, or worse than they were in May. The percentile standings for wholesaling show sales compared to a year ago at a 7.4 percentile standing, orders compared to a year ago at a 3.2 percentile standing, and sales for the time of year at a 1.8 percentile standing. All of these are simply exceptionally weak.
Expected sales volumes in wholesaling: Turning to the expected sales for August once again, all the readings are net negatives; two out of three of them show some improvement compared to their July values; however, the rankings remained exceptionally weak. Sales compared to a year ago are at a 9.1 percentile standing, orders compared to a year ago are at a 5.3 percentile standing, and sales for the time of year are at a 2.1 percentile standing. The results for expected sales and orders in the wholesaling survey are extremely grim.


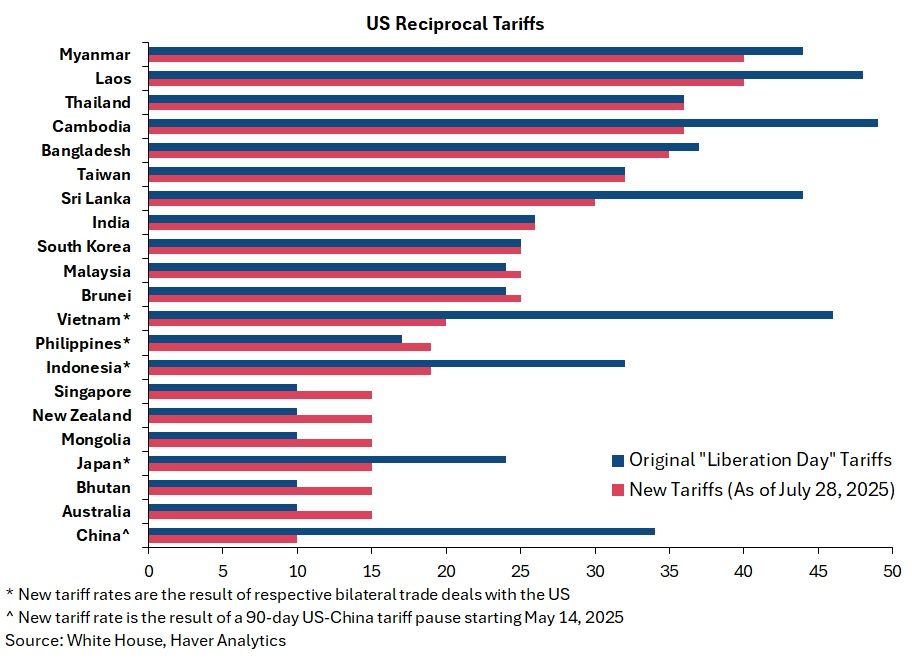
 Asia
Asia